Harnessing Advancement: RainierGPR Concrete Scanning for Accuracy Outcomes
Harnessing Advancement: RainierGPR Concrete Scanning for Accuracy Outcomes
Blog Article
Exploring the Depths: A Comprehensive Overview to Concrete Scanning and Its Diverse Applications
In the world of building and construction and framework development, the thorough process of concrete scanning holds an essential duty in making certain the architectural honesty and security of tasks. As modern technology proceeds to progress, the applications of concrete scanning have actually expanded much past plain surface-level assessments.
Significance of Concrete Scanning
Recognizing the significance of concrete scanning is important in guaranteeing the safety and honesty of frameworks during construction and improvement jobs. Concrete scanning uses advanced technologies such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electromagnetic induction to spot embedded objects, voids, or other anomalies within concrete structures.
Furthermore, concrete scanning plays a pivotal role in making sure compliance with building ordinance and guidelines that mandate the defense of existing structural parts during building and construction tasks. By accurately drawing up the inner composition of concrete, scanning modern technologies enable building and construction professionals to make enlightened choices that support the structural stability and toughness of structures and framework jobs. Basically, the significance of concrete scanning hinges on its capability to safeguard both the structural honesty and the workers involved in building undertakings.
Technologies Made Use Of in Concrete Scanning
Concrete scanning depends on innovative innovations such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electro-magnetic induction to accurately identify ingrained things and abnormalities within concrete frameworks. Ground-penetrating radar runs by giving off high-frequency electromagnetic waves into the concrete.
Electromagnetic induction, on the other hand, works by producing magnetic fields around a concrete structure via a transmitter coil. When steel items exist within the concrete, they interrupt these magnetic fields, triggering eddy currents to move with the steel. By measuring the modifications in the magnetic fields with a receiver coil, the system can pinpoint the area of metallic items in the concrete.
These innovative innovations play a critical duty in non-destructive testing, ensuring the safety and security and stability of concrete structures in various industries.
Applications in Construction Market
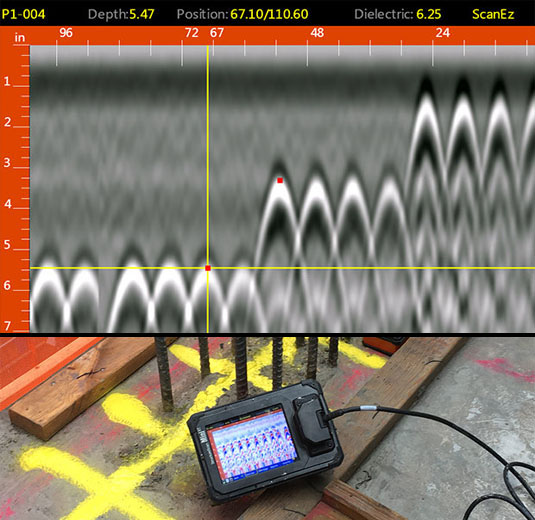
Within the building and construction industry, concrete scanning innovation locates varied applications that boost task effectiveness and safety and security. One crucial application is the discovery of rebar, post-tension cords, and other ingrained things before drilling or reducing right into concrete structures. By precisely mapping out these aspects, building teams can avoid expensive damages, make sure architectural honesty, and stop possible safety and security risks. In addition, concrete scanning is utilized for finding voids, such as air pockets or areas of degeneration within concrete, which can jeopardize the overall strength of a structure. By determining these voids beforehand, building professionals can take needed actions to address them and keep the resilience of the structure. Concrete scanning plays a crucial function in top find more information quality control by verifying the thickness of concrete covers over support, guaranteeing conformity with layout requirements and standards. In general, the applications of concrete scanning in the building sector add significantly to enhancing project process, lowering dangers, and supplying top notch results.
Safety And Security Benefits of Concrete Scanning
In the world of building safety, the execution of concrete scanning innovation offers a critical benefit in preemptively determining possible risks and fortifying architectural stability. By utilizing advanced scanning methods such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electromagnetic induction, building groups can properly locate rebar, post-tension cords, avenues, and various other hidden items within concrete frameworks. This positive strategy considerably lowers the risk of unexpected strikes throughout drilling, cutting, or coring tasks, thereby preventing pricey problems, injuries, and project delays.
Moreover, concrete scanning boosts employee safety and security by supplying real-time info concerning the architectural problem of concrete components. This information allows building and construction professionals to assess the stability of existing structures, determine degeneration or defects, and make notified choices pertaining to repair work and upkeep procedures. By dealing with possible safety problems immediately, concrete scanning adds to producing a protected working setting and reducing the probability of structural failures or mishaps on construction websites. Eventually, the safety benefits of concrete scanning not only guard lives and possessions however also support sector standards for top quality and dependability.
Future Patterns in Concrete Scanning
Emerging advancements in scanning innovation are positioned to transform the field of concrete examination and analysis. By harnessing the power of AI, these systems can assess huge amounts of information accumulated throughout scanning processes to give even more thorough and exact understandings right into the problem of concrete frameworks.
An additional substantial pattern is the advancement of even more mobile and user-friendly scanning tools. Miniaturization of scanning devices permits easier accessibility to confined spaces and remote areas, making examinations extra reliable and detailed. Additionally, advancements in wireless communication technologies enable real-time data transfer and analysis, assisting in quicker decision-making procedures.
Additionally, there is an expanding focus on sustainability in concrete scanning technologies - RainierGPR Visit Website Concrete Scanning. Makers are progressively this including environmentally friendly materials and energy-efficient attributes into their tools to lower environmental effect. These future trends are readied to improve the performance, accuracy, and sustainability of concrete scanning methods, shaping the market's future landscape
Verdict
To conclude, concrete scanning plays a critical function in the building and construction sector by guaranteeing the safety and effectiveness of various projects. By using innovative technologies, such as GPR and radar imaging, experts are able to precisely find possible threats within concrete structures. The applications of concrete scanning are substantial and proceed to advance, making it a necessary device for maintaining the integrity of buildings and facilities. As modern technology developments, the future of concrete scanning holds promising advancements for enhancing construction processes.

Report this page